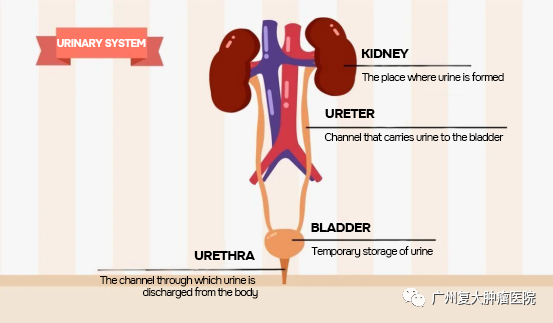
The genitourinary system refers to the urinary and reproductive systems. The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract, includes two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder, and the urethra.
The reproductive system includes external and internal genitals. The male internal reproductive system mainly includes testicles, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts, seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands.The types and causes of genitourinary system diseases are complex, which bring inconvenience and pain to patients' daily lives. Those "unspeakable" diseases always keep patients from seeking medical help in time.
01 What are the common diseases of the genitourinary system?
Infection
Urinary tract infection, also known as urinary system infection, is an inflammatory response of the urothelium to bacterial invasion, usually accompanied by bacteriuria and pyuria. The kidneys and ureters are the upper urinary tract, while the bladder and urethra are the lower urinary tract. The urethra and bladder are closely connected, so urinary tract infection can also cause bladder inflammation.
Male reproductive system infections mainly including prostatitis and epididymitis:
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate, which can be roughly divided into acute and chronic, usually caused by bacterial or non-bacterial infections. The main symptoms include painful urination, white urine, burning urine, frequent urination, and distended pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen and perineum; in severe cases, it may cause fever.
Epididymitis is seen more common in young and middle-aged male. It is often caused by the spread of urinary tract infection, prostatitis, and seminal vesiculitis. The infection is mostly transmitted retrogradely from the vas deferens. The systemic symptoms are obvious, including chills and high fever, and the scrotum is swollen and painful on the affected side.
Prostate disease
Prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer are common prostate diseases. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the most common benign disease causing urinary disorders in middle-aged and elderly men. The main manifestations are histological hyperplasia of prostatic interstitial and glandular components, anatomical prostate enlargement, lower urinary tract symptoms, and urodynamic bladder outlet obstruction.
With the improvement of living standards, the incidence of prostate cancer in men is increasing year by year. Prostate cancer often has no special symptoms in its early stages. When cancer cells grow, the prostate becomes enlarged and could squeezes the urethra, causing difficulty in urination. These cancer cells can spread through the bloodstream to other parts of the body. The course of the disease generally progresses slowly, and in the late stage it can cause symptoms such as bladder neck obstruction and distant metastasis.
Tumor
Tumors can occur in any part of the urinary system including the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, and urethra. They are generally divided into two categories:
One is tumors of the hollow organs like the renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, and urethra. The lumen is covered with urothelium, so the most common tumors of the urinary system is transitional epithelial tumors.
The other type is non-urothelial tumors in various organs like renal cancer and kidney parenchyma, such as bladder rhabdomyosarcoma.
Stones
Urinary stones are a common disease of the urinary tract. Stones can be seen anywhere in the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra, kidney and ureteral stones are the most common types. Clinical manifestations vary depending on the location of the stone. The typical manifestations of kidney and ureteral stones are renal colic and hematuria. Before the onset of colic caused by the stones, the patient does not feel anything. However, certain inducements, such as strenuous exercise and long-distance driving could cause severe pain in stone side of the waist suddenly and radiates to the abdomen and perineum, accompanied by abdominal distension, nausea, vomiting, and varying degrees of hematuria; bladder stones are mainly characterized by difficulty urinating and painful urination.
02 How to prevent urinary diseases?
The genitourinary system is an important organ system of the human body. It not only affects our excretory function, but also affects our blood pressure, water balance, red blood cell production, etc. The health of the urinary system is closely related to our quality of life. If there is a problem, it will bring us a lot of inconvenience and trouble, and even threaten our lives. Therefore, we should pay attention to urinary health and take the following actions:
Drink more water
Drink at least 2000ml of water every day to maintain adequate urine output, flush the urinary tract to prevent infection and stones.
Keep balanced diet
Eat less foods high in calcium, high oxalic acid, and high purine, and eat more foods rich in vitamin C and fiber to regulate the acid-base balance in the body.
Keep hygienic
Clean the perineum every day and keep it dry to avoid bacteria.
Periodic inspection
Conduct urinary system examinations at least once a year to detect and treat urinary system problems in early stage.
When the following symptoms appear
Please seek medical help promptly
Urine abnormalities:
Hematuria, pyuria, chyluria, etc.
Urination symptoms:
Frequent urination, urgency, painful urination, difficulty urinating, urinary incontinence,
Urinary leakage, enuresis, interruption of urine flow, etc.;
Pain:
Waist and abdominal pain, lower abdominal pain, suprapubic area and perineal pain, scrotal area pain, etc.;
Lumps:
Lumps in the upper abdomen and waist, masses in the lower abdomen, and groin areas,
Masses in the scrotum, penis, etc.;
Urethral discharge:
Purulent, mucus, bloody and other secretions;
Sexual dysfunction:
Difficulty in erection, low desire, premature ejaculation, painful ejaculation, hematospermia, etc.