The breast is an important part of the female body, playing a positive role in women’s confidence and mental health. However, in recent years, breast health issues among women have become increasingly concerning. Statistics show that the incidence of various breast problems in women aged 25 and above is as high as 70%, and it’s over 80% for women of childbearing age. Among these, breast cancer ranks first in cancer incidence among women nationwide, making it one of the leading killers of women.
So, how should women deal with breast health in daily life? How can they "care for and maintain" their breasts? Recently, Dr. Wang Feng, Deputy Chief Physician and Deputy Director of the Second Medical Department at Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital, shared prevention and treatment strategies for breast diseases.

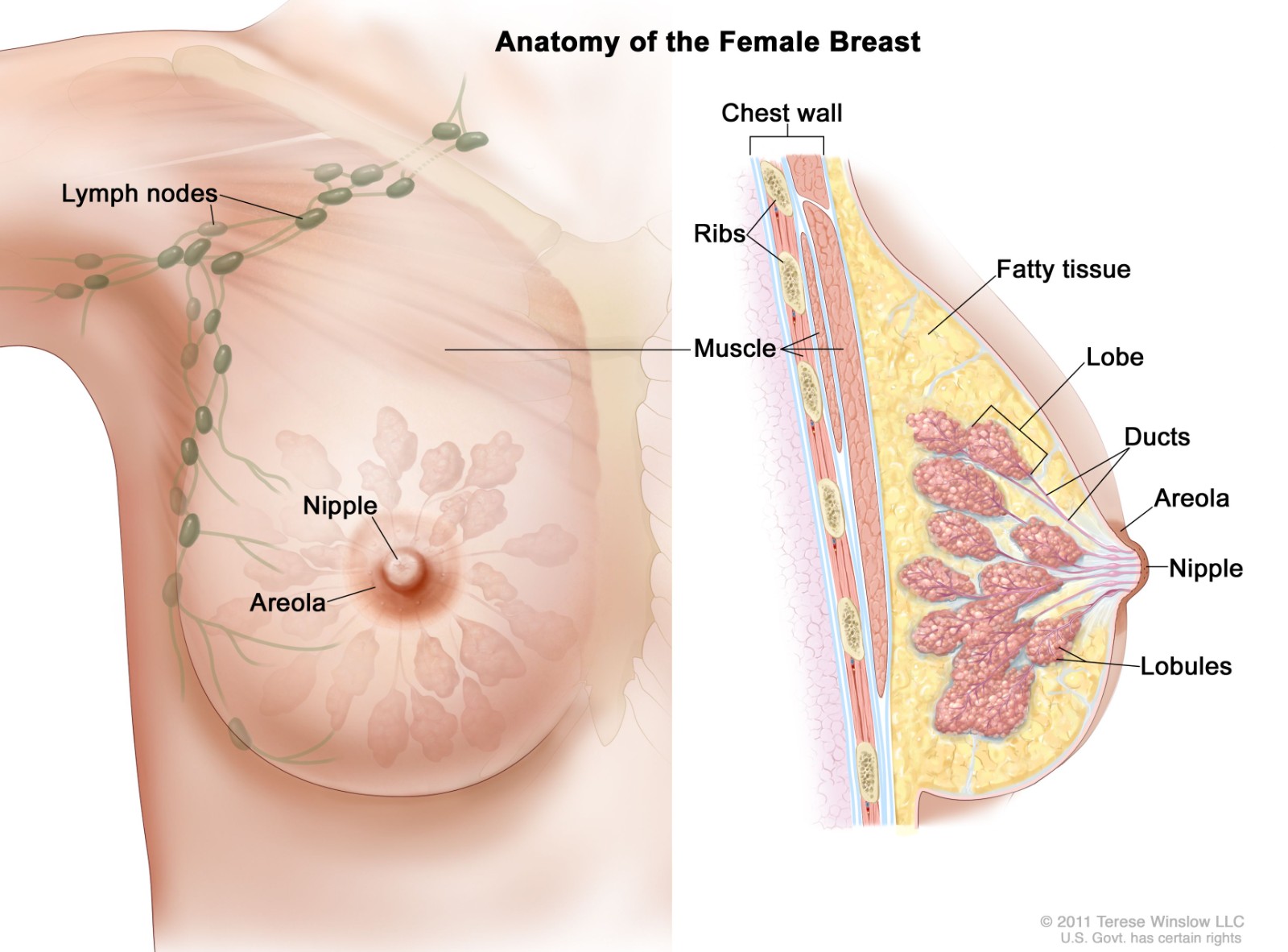
Common Breast Diseases
Breast Hyperplasia
Breast hyperplasia is the most common breast disease. It is neither an inflammatory condition nor a tumor. It presents as cords, lumps, or cystic nodules in the breast, with pain as the primary symptom. This condition results from incomplete physiological hyperplasia and involution, leading to structural disorder in the breast.
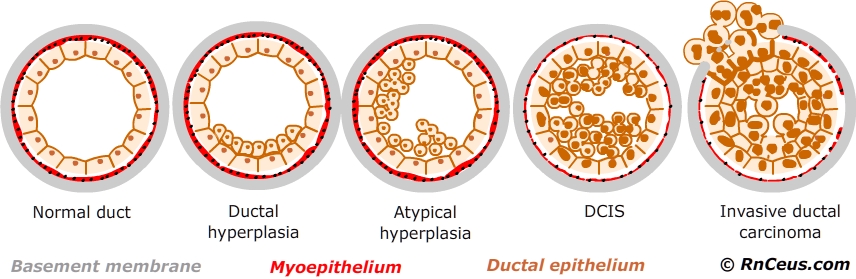
Breast hyperplasia often occurs or worsens before menstruation, mainly affecting women aged 30-50. Although it rarely progresses to malignancy, rapid growth or hardening of a single lump could suggest malignancy. The condition is generally linked to hormonal imbalances and factors such as stress and environment.
There is no specific treatment for breast hyperplasia, and most cases resolve on their own within months to a couple of years. If symptoms are severe, wearing a bra for support and avoiding spicy food may help. Medications like traditional Chinese medicine (Xiaoyao San), androgen, or tamoxifen may be prescribed. If these treatments fail and local lesions change significantly, a biopsy is recommended. If there is significant epithelial hyperplasia, a simple mastectomy can be performed, while malignant transformation may require a radical mastectomy.
Misconceptions About Breast Hyperplasia
- Misconception 1: If the lump is painless, there is no need to worry about it.
- Misconception 2: It will naturally resolve after having another child or after menopause.
- Misconception 3: Once the pain is gone after treatment, no further treatment is necessary.
- Misconception 4: Only women can develop breast hyperplasia; men cannot.
- Misconception 5: Treatment relies solely on medication.
- Misconception 6: Breast hyperplasia will always turn into breast cancer.
- Misconception 7: Women with small breasts are immune to breast hyperplasia.
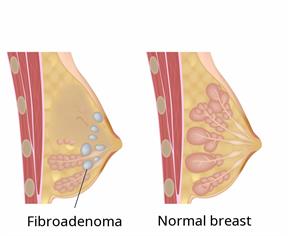
Fibroadenoma of the Breast
Fibroadenoma is a benign tumor, mostly seen in women aged 20-30. It is related to hormonal imbalances and can occur in one or both breasts, usually as a single tumor. The main clinical symptom is a breast lump, which is often painless and does not change with the menstrual cycle.
Maintaining a positive mindset, healthy lifestyle, and regular habits can help prevent breast diseases. Wearing well-fitted bras, avoiding tight or constrictive clothing, and practicing good hygiene are important. Cotton bras with good breathability and absorbency are recommended, and it’s best to avoid wearing a bra during sleep.
Breast Cyst
Breast cysts, also known as milk retention cysts, occur during lactation when milk accumulates in the breast due to poor drainage from a glandular lobe. Clinically, they appear as breast lumps and are often misdiagnosed as breast tumors. Factors like previous hyperplasia, inflammation, or tumors can block the ducts, leading to cyst formation.
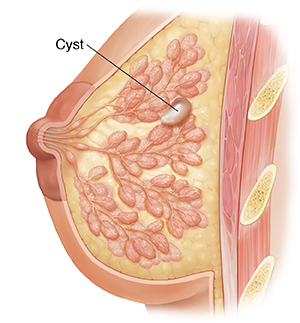
Patients should avoid high-fat foods and prevent obesity. It's important to limit the use of estrogen-containing medications and avoid excessive use of contraceptives or beauty products with estrogen. Foods like seaweed may help reduce pain and shrink lumps, while cold or spicy foods should be avoided.
Mastitis
Mastitis is an acute bacterial infection of the breast, often caused by bacteria entering through nipple cracks or milk ducts. It mostly occurs in women breastfeeding after their first childbirth, usually within 3-4 weeks postpartum. Symptoms include fever, chills, breast swelling, pain, and abscess formation.
Treatment includes infection control and milk drainage. Before abscess formation, antibiotic treatment is key. If an abscess forms, surgical drainage is necessary. Heat compresses can help reduce inflammation and swelling, regardless of the stage of the condition.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that arises from the epithelial tissue of the breast. Its early symptoms are not obvious, typically manifesting as a hard lump the size of a pea, often without pain. Other signs include nipple retraction, skin dimpling (peau d'orange), and ulceration.
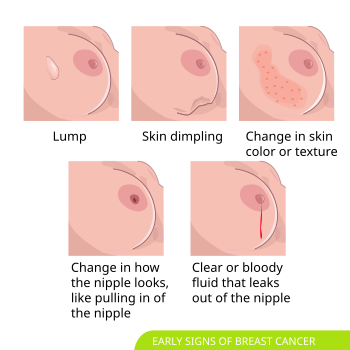
Women with the following risk factors have a higher risk of developing breast cancer:
- Early menarche (before age 12) or late menopause (after age 55), nulliparity, late childbirth (after age 35), or not breastfeeding;
- A family history of breast cancer;
- High estrogen levels, use of contraceptives, or long-term hormone replacement therapy;
- Atypical breast hyperplasia;
- Obesity, high-fat diet, excessive alcohol consumption;
- Prolonged stress, anxiety, depression, frequent night shifts, or smoking.
Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, and molecular targeted therapy. Modern treatment trends include minimally invasive surgery, precise stereotactic radiation, and targeted drug therapy.
Women should adopt a low-fat, vitamin-rich diet and maintain balanced nutrition to reduce the risk of breast diseases. Foods like cabbage, soy products, seaweed, fish, and yogurt are beneficial. Women should also avoid excessive use of estrogen-containing products.