When it comes to the incidence rate of all malignancies, lymphoma is not the highest; however, when it comes to growth rate, lymphoma will surely come out top. The statistics shows that the incidence rate of lymphoma in China is increasing by 5% every year and there are 50,000 new lymphoma patient diagnosed each year. Though lymphoma has become one of the top 10 malignancies in China, the public is still lacking of awareness of lymphoma and is not paying enough attention to it.
Two categories of lymphoma
All lymphomas are malignant and the only difference is the degree of malignancy. The peak period of incidence among people is 45 to 60 years old. The incidence rate of lymphoma will increase accordingly as people grow old. Its pathogenesis is not completely known yet. Risk factors for lymphoma include EB virus infection, aggravated environment pollution, long-term exposure to electron radiation, etc.
According to Dr. Wen Weifeng of Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital, lymphoma is classified into two main categories, Hodgkin lymphomas (HL) and the non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL). In China, the incidence rate of NHL is much higher than that of HL. As there are dozens of subtypes of lymphoma which can be easily neglected due to their occult onset, lymphoma patients tend to miss the prime treatment opportunity if it cannot be detected at early stage and get correct diagnosis. Luo Jing, a famous anchor of CCTV News, was also died of lymphoma.
Among all diagnosed NHL patients, 45% belong to the category of indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and 55% belong to the category of aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Signs and symptoms
Lymphoid tissue is present in places wherever there are body fluids, which means that lymphoma may present throughout the body, such as lung lymphoma, gastric lymphoma. Clinical manifestations of lymphoma vary because of the different invading sites.
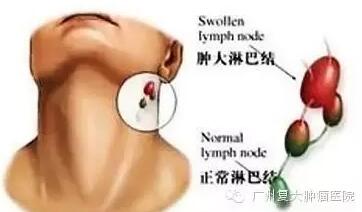
★Local manifestation
(1) Lymphadenopathy: it includes superficial and deep lymph nodes enlargement. The swelling lymph nodes are painless, hard in texture with good mobility. Lymph nodes are not adhered to each other at early stage but fuse to each other at late stage. Anti-inflammatory and anti-TB treatment show futile. Superficial lymph nodes are most seen in neck and then in axilla and groins. Deep lymph nodes are most seen in mediastinum and beside aorta abdominalis.
(2) Lymph nodes enlargement causes local compression: deep lymph nodes are mainly involved. Mediastinal lymph nodes enlargement compresses esophagus to dysphagia; compression of trachea causes cough, chest distress, breathing difficulty, etc. (when compressive symptoms are present, it suggests that the disease has been very serious)
★ Systemic symptoms
(1) Fever: persistent low fever or periodic fever with unknown cause.
(2) Weight loss: most patients show weight loss and the body weight reduces by 10% within 6 months.
(3) Night sweat
★ Invasion of general tissues and organs
For instance, invasion of liver and spleen causes hepatosplenomegaly; invasion of lung and pleura causes cough, pleural effusion; bone invasion causes ostalgia and pathological fracture; bone invasion causes skin itching and subcutaneous nodule; pharyngeal invasion causes dysphagia, etc.
Dr. Wen Weifeng reminded that if the symptoms, such as repeated fever, weight loss, lymphadenopathy are persistent, an evaluation to determine their cause should be undertaken.
❤ Standard treatments determine the curative effect
The first words come to people’s mind would be incurable disease when it comes to malignant cancer. However, doctors noted that though the therapeutic effect for different subtypes of lymphoma vary, the overall curative effect of lymphoma has been elevated to be the best among all malignant cancers. Early diagnosis, correct classification and standard treatment are the key to good therapeutic effect.
To make a definite diagnosis mainly needs pathological examination, imageological examination, nuclear medical examination, blood biochemical examination, etc. However, the final diagnosis should take pathological examination result as the “golden standard”. That means the type of lymphoma can only be verified by pathological examination in the form of surgical collection or fine needle aspiration whether the lymphoma happens to lymph nodes or other organs. Only by doing so, the correct treatment can be undertaken accordingly.
At present, the main treatments for lymphoma include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation. Immunotherapy is also applicable to certain patients.
Expert profile

Wen Weifeng currently serves as the Deputy Director of the ICU of Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital. After graduating from Hunan University of Chinese Medicine as an integrated western and Chinese medicine major, he started to engage in clinical work firstly at Guangdong No. 2 Provincial People’s Hospital and then at Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital. He received training at the ICU of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. With a solid medical foundation, he can well handle common clinical diseases and frequently encountered diseases in medical oncology. He has accumulated certain experience in the rescue and treatment of critically ill patients and gained his attainment in treating complications brought by chemotherapy. He has an in-depth understanding of lymphoma and myeloma and has cured several cases of this kind.