First Medical Department of Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital admitted a patient with lung nodules.
The patient, Uncle Qiao (pseudonym), is nearly 70 years old. He suffered from asthma and burning sensation in his lungs when he exercised a lot. In March 2021, he went to a local hospital for examination and was found to have a nodule in the inner basal segment of the right lower lobe of the lung, which tended to increase in size, and malignant tumor lesions could not be ruled out.
Uncle Qiao went to many hospitals and was basically told that he needed surgery, that is, to remove the lower lobe of the right lung, but the postoperative pathological results might also be benign. In order to reduce trauma, Uncle Qiao refused surgery and looked for new treatment methods. It was not until he learned about the application of cryoablation technology in lung nodules and lung cancer at Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital that Uncle Qiao decided to come to our hospital for treatment.
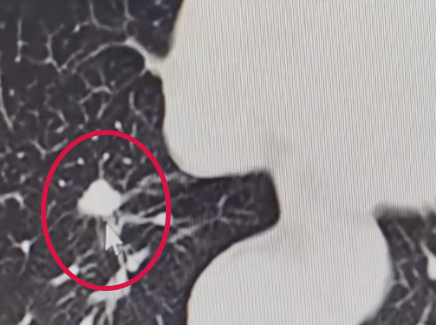
▲Preoperative CT scan on May 15, 2023
Before the consultation, Uncle Qiao listed all his doubts about cryoablation as questions, such as: Is it suitable for basal segment nodules? How to obtain pathological tissue? Is the recurrence rate high after surgery? ... In response to Uncle Qiao's questions, our hospital's director Niu Lizhi answered them one by one.
For the treatment of lung nodules, according to the NCCN guidelines, surgery is still the first choice. However, not all patients with lung nodules can undergo surgery. If the patient is unable to undergo surgery or refuses surgery due to old age, poor cardiopulmonary function, multiple lung nodules, or postoperative recurrence and metastasis, cryoablation is a good choice for this situation.
Cryoablation is more advantageous for lung nodules that are relatively central, adjacent to, or invade the mediastinum or chest wall. Especially when close to the chest wall, cryoablation causes less pain stimulation to the body. While freezing the tumor to death, it does not easily form "lung cavities" like thermal ablation. At the same time, simultaneous cryoablation with lung puncture biopsy can solve the diagnosis and treatment needs at one time, and can reduce the risk of pneumothorax and bleeding caused by repeated punctures, avoid the intensive open-chest surgery, and do not affect the patient's daily life. Radiotherapy and (or) chemotherapy can also be continued after surgery.
In addition, the double-probe method of cryoablation can fix lung nodules, improving the accuracy, success rate and efficiency of cryoablation for small lung cancers. When the edge of the frozen ice ball is 1.0 cm larger than the edge of the tumor, the nodules can achieve a satisfactory clinical effect. After a lot of research and practice, Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital has optimized lung tumor ablation with three-cycle cryoablation technology, which has been proven to have a lower recurrence rate and complication rate.
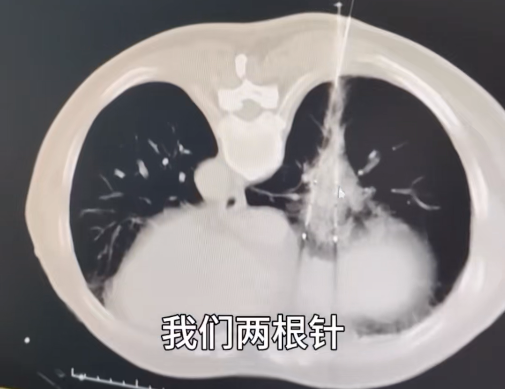
▲Double-needle clamping of lung nodules during surgery on May 16, 2023
Combined with previous examinations, the size of the nodule in the basal segment of the right lower lobe of Qiao Shu was about 1.1×0.8cm, with adhesions and traction of the adjacent pleura, and local adhesions with the bronchus and artery. In order to locally inactivate the tumor and clarify the diagnosis, Qiao Shu underwent simultaneous puncture biopsy and cryoablation. The operation went smoothly, and the postoperative pathological results showed: (right lung) adenocarcinoma in situ.
At present, the CT scan of Uncle Qiao shows that no new lesions were found in his chest, and the solid components of the lung nodules have disappeared. For him, this treatment not only solved his nodules, but also preserved his lung lobes, and did not cause much impact on his exercise, breathing and life.
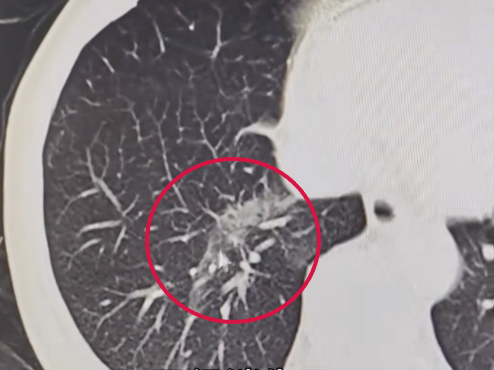
▲CT scan after surgery on May 23, 2024
[Expert Said] Pay attention to early screening of lung nodules, but don’t panic too much
At present, there are 150 million people at high risk of lung nodules in China, and 10 to 20 million new lung nodules are discovered or diagnosed each year. Early screening of lung nodules is also the most common problem in clinical practice. In the past two years, many people have found that the proportion of themselves and people around them who have lung nodules during CT scans has also increased. Recently, Zhong Nanshan, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, accepted an exclusive interview with CCTV News and answered some questions about lung nodules.

▲The picture comes from CCTV News
In the interview, Academician Zhong Nanshan first pointed out two main reasons for the increase in the detection rate of lung nodules: on the one hand, due to the impact of the new crown, many people underwent CT examinations due to symptoms such as fever and cough, which greatly increased the number of people undergoing CT examinations. As an important means of early screening of lung nodules, the increase in the popularity of CT has naturally led to an increase in the detection rate of lung nodules.
On the other hand, pulmonary nodules are actually quite common in adults. According to statistics, about 30% to 40% of normal people have nodules of varying sizes. When we apply artificial intelligence technology to CT scans, we even find that 60% of people have pulmonary nodules.
Although the detection rate of lung nodules has increased, Academician Zhong Nanshan stressed that the public does not need to panic. He pointed out that most lung nodules are benign, and only a few may develop into lung cancer. Therefore, attention to lung nodules is necessary, but excessive worry and fear are unnecessary. With the continuous advancement of medical technology, more accurate examinations can be used to distinguish between benign and malignant nodules, so as to develop more scientific and effective diagnosis and treatment plans.
