The Nanoknife System is a nonthermal and novel minimally-invasive technology for tumor ablation. It is also known as Irreversible Electroporation (IRE). Its rationale goes like as follows: during the procedure, high electric-field and ultrashort pulses are given to destroy lipid bilayer structure of cancer cell membrane and form numerous irreversible nano-sized pores in the cell membrane. Cell membrane permeability will be changed to allow molecules of different sizes free access to cells, which will lead to cell death.
Nanoknife Therapy can be applied to treat tumors in solid organs such as pancreas, liver, lung, kidney and prostate, and is especially suitable for tumors adjacent to the great blood vessels, hepatic hilar region, gallbladder, bile duct and ureters. Nanoknife Therapy has been approved by America FDA in October 2011 and European Union for clinical application respectively in December 2012. In June, 2015, it has been approved by China for clinical application. Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital become the first in Mainland of China to introduce Nanoknife Therapy and successfully completed the first case of Nanoknife treatment on July 1. Professor Xu Kecheng and Professor Niu Lizhi compiled a book called New Technique of Cancer Ablation – Irreversible Electroporation, the first book on Nanoknife in mainland China.
Development of IRE
IRE was created by an American company, AngioDynamics and was applied to the ablation of soft tissue tumor after approved by America FDA in 2011, which attracted the attention of experts all over the world. Afterwards, it was approved in UN, Australia, Canada and China. So far, there have been over 100 cancer hospitals that adopt this technique. The tumors treated include tumors of the pancreas, liver, kidney, prostate and other parenchymal organs and soft tissues, especially those adjacent to the great blood vessels, hilar region, gallbladder, bile duct and ureters. The literature reports special value in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Rationale
Nanoknife tumor therapy is a new technique which is popular in recent years. It refers to inserting a 1mm-diameter electrode needle through the skin into the tumor, and calculating and mapping the expected electric field by computer technology, releasing high-voltage electrical pulses to make a permanent perforation at the nanoscale on the tumor cells, disrupting the intracellular balance and causing the rapid apoptosis of the target cells (cancer cells). Because cell perforations are nanoscale, it is called Nanoknife Therapy.
Tumor ablation is a major advance in the treatment of cancer in the 21st century, enabling many patients who cannot receive surgery or who are not resistant to surgery, to obtain effective treatment and even radical treatment. Common techniques include thermal ablation (radiofrequency and microwave ablation) and cold ablation (argon-helium knife and liquid nitrogen). Nanoknife is a special technology that is neither hot nor cold. If we compare “ablation” to the "crown" of local tumor treatment, Nanoknife is the "pearl" on the crown.
How IRE works
A series of experimental and clinical studies have shown that Nanoknife has advantages that other ablation techniques do not process, including the selective ablation of tissue, which only damages "cells" and rarely damages vascular walls, nerves, trachea and bronchus, bile ducts, intestines and ureters. The ablation zone is well defined. This is important for the small pancreas: ablation does not produce heat, nor does it rely on heat, nor is it affected by the flow of adjacent large vessels (e.g., celiac artery, aorta).The cell death is not necrosis, but apoptosis, which can stimulate anti-tumor immune response. The treatment time is very short, only 5 minutes needed for the treatment of 3cm tumor, and the anesthesia time is correspondingly shortened, which is conducive to postoperative rehabilitation. The ablation process can be clearly displayed on ultrasound, CT or MR to ensure the best result.
Nanoknife releases a high voltage pulse on the tumor cells through a probe, causing irreversible electroporation of the cell membrane at the nanoscale, which leads to cell apoptosis. After tumor cell apoptosis, phagocytic cells in the body engulf the cell debris, and the treatment area is gradually replaced by normal tissue.
Nanoknife Therapy can more precisely induce tumor cell apoptosis, which has made thorough tumor ablation possible. It inflicts no irreversible damage to other important tissues in ablated area, such as vessels, bile duct and nerves; therefore, complications caused by other traditional ablation methods will be reduced. Therefore, Nanoknife Therapy can be applied to treat tumors in solid organs such as pancreas, liver, kidney and prostate, and is especially suitable for tumors adjacent to great blood vessels, hepatic hilar region, gallbladder, bile duct and ureters.
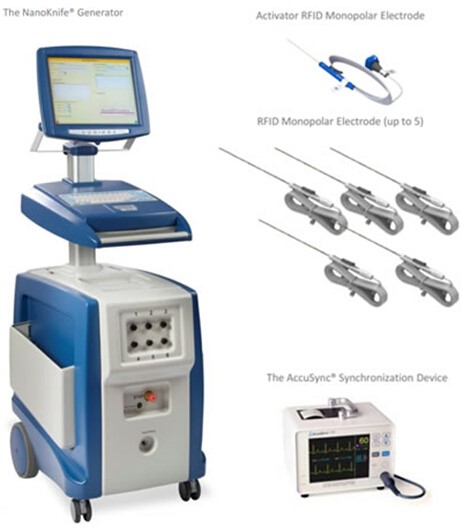
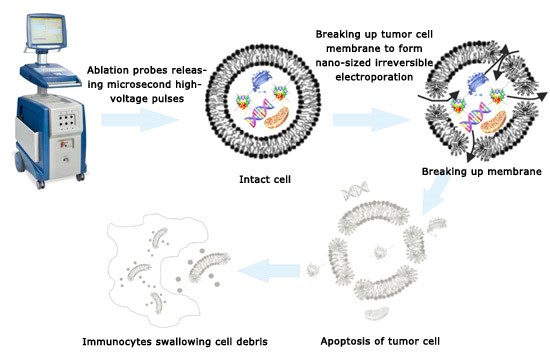
Nanoknife system for tumor ablation The Rationale of Nanoknife Therapy
Advantages
Based on numerous clinical studies, Nanoknife Therapy is a safe and effective technology for tumor treatment. It boasts the following advantages:
1. Short ablation duration
For solid tumors about 3 cm in diameter, it requires just 90x100milisecond ultrashort pulses. One group of treatment takes less than one minute. Even if there are 3 to 4 overlapped ablation areas, the whole ablation duration will be less than 5 minutes.
2. Preserving important tissues such as vessels and nerves in ablated areas
Nanoknife Therapy can protect important tissue structures in ablated areas. Important liver structures, such as hepatic artery, hepatic vein, portal vein and intrahepatic bile ducts can be well protected after being treated with Nanoknife Therapy.
3. No heat island effect
Nanoknife System for tumor ablation uses electrical pulses to breakdown cell membrane. The procedure will neither generate energy nor be influenced by external temperature. While during traditional thermal ablation or cryoablation, energy will be taken away by blood flow if there are big vessels in ablated areas, which will lead to incomplete ablation in surrounding area.
4. Thorough ablation with clear dividing line
IRE will perform thorough ablation to tumor whether it’s close to vessels or irregular and big in size. Moreover, there is a clear dividing line between ablated area and non-ablated area that is only about 1 to 2 cell units in thickness. Therefore, more precise judgment and evaluation can be made for the follow-up, effectiveness and treatment performance of Nanoknife Therapy.
5. Ablated area will remain functional
Nanoknife will cause irreversible damages to tumor cells and induce cell apoptosis. Cell apoptosis is able to stimulate immunity to promote cell death. Human body will identify cell apoptosis as normal cell death and then clean apoptotic tissue through cytophagy so as to promote the regeneration and repair of normal tissue.
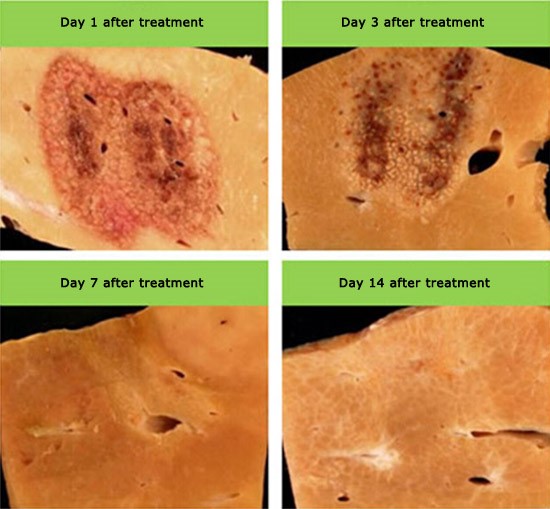
No heat island effect with good postoperative recovery
6. Real time monitoring during treatment
Nanoknife Therapy can be navigated and monitored by ultrasound, CT or MR. There is only few millimeters of difference in size between ablated areas monitored by ultrasound or CT and that measured in pathological analysis. The imaging can also clearly display unablated residual cancer cells, to which doctors can perform ablation again. Moreover, real time monitoring allows doctors to observe the changes in the surrounding tissues of ablated area and predict the possibility of complications so as to guarantee patient’s safety and quick postoperative recovery.
7. Nanoknife Therapy can be applied to more complicated conditions
Traditional ablation cannot be adopted when tumor is close to such areas as big vessels, bile duct, pancreatic duct and hepatic portal vein. Ablation would also cause nerve damage that will lead to paralysis and loss of sexual ability if cancer happens to prostate or close to spine. As Nanoknife Therapy inflicts no damage to canals and nerves and delivers secure and effective treatment for the above-mentioned cases, it plays an irreplaceable role for these patients.
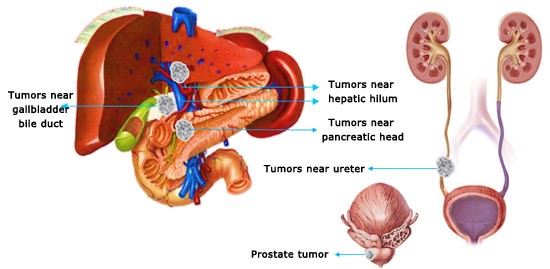
Nanoknife Therapy can be applied to cases that other types of ablations can’t manage